Colon polyps are more or less large masses of tissue that project into its cavity, that is, in the lumen.
Apart from some inflammatory polyps also called pseudopolips the others are neoplastic.
INDEX:
1. WHAT IS COLON
2. WHAT ARE COLON POLYPS
3. PROCEDURE FOR DIAGNOSIS
4. COLON CARCINOM SYMPTOMS
5. SURGICAL TECHNIQUES
5.1 LAPAROSCOPIC COLON RESEARCH
6. INFORMATION AFTER THE LAPAROSCOPIC COLON RESEARCH OPERATION
1. WHAT IS COLON
The Colon is that intestine stretch that extends from hoof to anus.
It is divided into Right Colon and left Colon.
The Right Colon in turn is divided into Czech, which receives the digested material from the heel, and represents the point where the appendix, Ascending Colon, Limb Flessure and right side of the transverse colon are present.
The Left Colon includes the left side of the transverse colon, splenic flexion, descending colon, sigmoid colon or sigma and the rectum representing the final part.
The digested food material is poured in liquid form from the heel in the Czech and with peristaltic contractions continues to the rectum.
In this pathway it is gradually dehydrated to be excreted in the form of stools from the anus.
One important function of Colon is to absorb water.
2. WHAT ARE COLON POLYPS
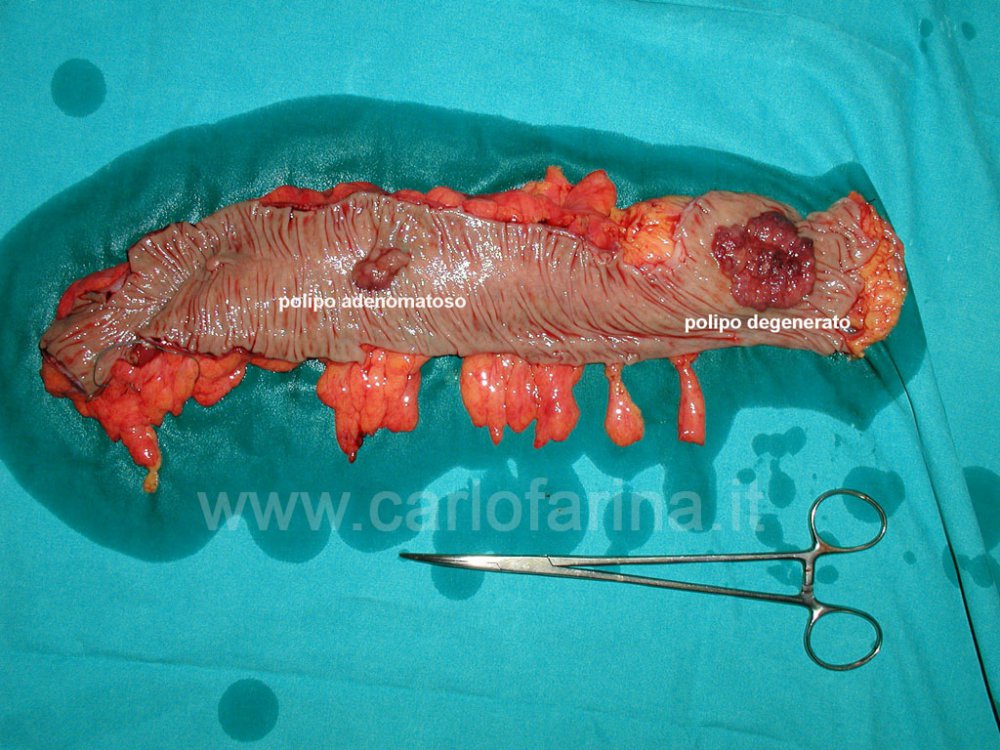
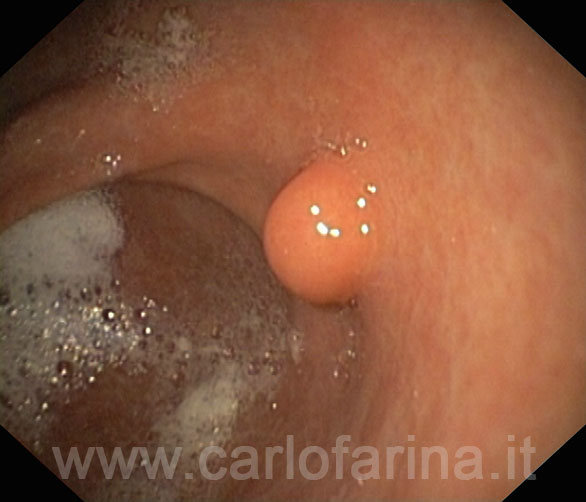
Colon polyps are more or less large masses of tissue that project into its cavity, that is, in the lumen.
Apart from some inflammatory polyps also called pseudopolips the others are neoplastic.
Their evolution is worse in the sense that they generally appear to be benign polyps (Adenoma) but over time they can evolve into carcinoma that represents the main colon cancer.
Most colon polyps are asymptomatic, sometimes occurring with blood loss with stools or with the search for OCCULATED BLOOD in the stools.
They are mostly found only with COLONSCOPY which can also be curative.
Many polyps, especially small ones, may be removed by the endoscopist.
To prevent colon cancer, we must all, men and women, have a colonoscopy over 50 years of age!
If there are family cases (parents, siblings, grandparents) who have colon or colon cancer, then colonoscopy is indicated at 40 years.
3. PROCEDURE FOR DIAGNOSIS
The Best Way to Examine the Colon is with Endoscopy.
Depending on whether or not part of the colon is examined, anorectoscopy, rectosigmoidoscopy or a complete colonoscopy is known as pancooloscopy.
In many centers this examination is performed in sedation, without warning the slightest pain.
For some years now, there is the possibility of performing a Virtual Colonoscopy with the aid of last generation TACs.
However, the indications for this examination are limited.
Always ask your doctor first if you are planning to do a virtual colonoscopy because you may still have to have an endoscopic colonoscopy!
4. COLON CARCINOM SYMPTOMS
Colon Cancer can be highlighted with these symptoms:
• Right Colon: Weakness, Asthenia or Anemia, Occult Blood in the Stomach, Digestion Maleness, Abdominal Abdominal Pain on the Right
• Left and right Colon: Alteration of intestinal habits, in the sense of the appearance of constipation or diarrhea that was not present before, blood also visible red in the faeces, intestinal occlusion symptoms with pain and gingivitis, feeling of incomplete evacuation with necessity To evacuate frequently.
As a lab data, 70% of patients with colon cancer have a blood increase in CEA value.
Before being subjected to colon resection surgery, it is necessary to complete the tests with a TAC examination.
5. SURGICAL TECHNIQUES
The treatment consists in resection of a more or less wide part of colon possibly with regional lymph nodes, taking care not to disperse tumor cells in the abdomen.
After the resection a suture of the two intestine tracts, the so-called anastomosis, is performed, which can be performed manually or with the help of sophisticated devices that cut and directly sew the tissues.
Colon resection is currently possible in most cases by Laparoscopic.
5.1 LAPAROSCOPIC COLON RESEARCH:
It consists in performing the colon resection surgery through the miniature inserts of 5 to 12 mm as the point of entry of an optic and instruments.
The abdomen is relaxed with gas (carbon dioxide).
Often, the so-called "service engraving" is necessary, a small opening of the abdomen generally above the pubis, to get the colon removed from outside.
The technique does not vary with the analogous "open", that is laparotomic, but is certainly more precise as it is performed with small and delicate instruments, with an enlargement of all tissues and with the need to limit blood loss, The reduced vision of the operating field.
It is recognized that those who undergo laparoscopic interventions have less need to translate